Web Usage
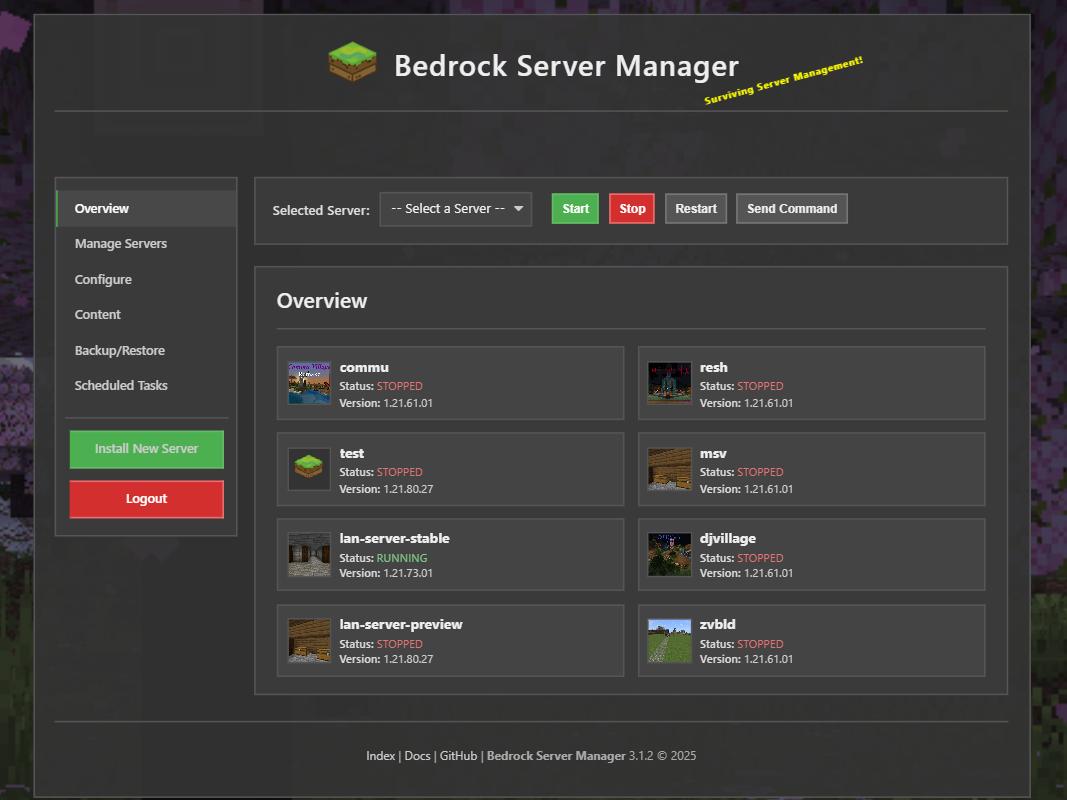
Bedrock Server Manager 3.1.0 includes a Web server you can run to easily manage your bedrock servers in your web browser, and is also mobile friendly!
With the web server you can:
Install New Server
Configure various server config files such as allowlist and permissions
Start/Stop/Restart Bedrock server
Update/Delete Bedrock server
Monitor resource usage
Install world/addons
Backup and Restore all or individual files/worlds
Hosts:
Note
As of BSM 3.5.0, the web server will only accept one host at a time, if multiple hosts are specified, the first one will be used.
By Default Bedrock Server Manager will only listen to local host only interfaces 127.0.0.1
To change which host to listen to start the web server with the specified host
Example: specify local host only ipv4:
bedrock-server-manager web start --host 127.0.0.1
Example: specify all ipv4:
bedrock-server-manager web start --host 0.0.0.0
You can also change the host by running the setup command, which will prompt you for the host to use.
bedrock-server-manager setup
Port:
By default Bedrock Server Manager will use port 11325. This can be change with the setup command.
HTTP API:
Note
As of BSM 3.5.0, the HTTP API docs are now integrated in the web server using FastAPIs Swagger UI.
Visit: http(s)://<bsm_host:port>/docs after starting the web server.
An HTTP API is provided allowing tools like curl or Invoke-RestMethod to interact with server.
Obtaining a JWT token:
The API endpoints require authentication using a JSON Web Token (JWT).
How: Obtain a token by sending a POST request to the /api/login endpoint.
Request Body: Include a JSON payload with username and password keys, matching the values set in the environment variables.
{
"username": "username",
"password": "password"
}
Response: On success, the API returns a JSON object containing the access_token:
{
"access_token": "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9..."
}
Tokens expiration is configurable via script_config.json (default: 4 weeks).
curl Example (Bash):
curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"username": "your_username", "password": "your_password"}' \
http://<your-manager-host>:<port>/api/login
PowerShell Example:
$body = @{ username = 'your_username'; password = 'your_password' } | ConvertTo-Json
Invoke-RestMethod -Method Post -Uri "http://<your-manager-host>:<port>/api/login" -Body $body -ContentType 'application/json'
Using the API
Endpoints requiring authentication will need the obtained access_token included in the Authorization header of your requests:
"Authorization: Bearer YOUR_JWT_TOKEN"
For requests sending data (like POST or PUT), set the Content-Type header to application/json.
Examples:
Start server:
curl Example (Bash):
curl -X POST -H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_JWT_TOKEN" \
http://<your-manager-host>:<port>/api/server/<server_name>/stop
PowerShell Example:
$headers = @{ Authorization = 'Bearer YOUR_JWT_TOKEN' }
Invoke-RestMethod -Method Post -Uri "http://<your-manager-host>:<port>/api/server/<server_name>/stop" -Headers $headers
Send Command:
curl Example (Bash):
curl -X POST -H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_JWT_TOKEN" -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"command": "say Hello from API!"}' \
http://<your-manager-host>:<port>/api/server/<server_name>/send_command
PowerShell Example:
$headers = @{ Authorization = 'Bearer YOUR_JWT_TOKEN'; 'Content-Type' = 'application/json' }
$body = @{ command = 'say Hello from API!' } | ConvertTo-Json
Invoke-RestMethod -Method Post -Uri "http://<your-manager-host>:<port>/api/server/<server_name>/send_command" -Headers $headers -Body $body